Electrocoagulation

WHAT IS ELECTROCOAGULATION
Electrocoagulation (EC) is an emerging technology in water and wastewater treatment because it combines the advantages of coagulation, flotation, and electrochemistry. It is an electrochemical process that uses electric current to remove suspended, emulsified, or dissolved pollutants from water. Electrochemi- cal wastewater treatment technology has begun to regain attention because it is an environmentally friendly option that can produce the least sludge, does not require chemical additives, and the smallest footprint, without affecting the water quality after treatment.
The main advantage of EC over other technologies like chemical coagulation/flocculation CC/CF is that coagulation/flocculation uses chemical coagulants/flocculants such as metal salts or polyelectrolytes. In EC, the coagulants are generated in situ by the electrolytic oxidation of an appropriate anode material which results in much less sludge generation. Compared with CC/CF and other conventional water treatment methods, another major advantage of EC is that it can treat oily water, where the presence of electric current can help the electrocoagulation of oil droplets. With several applications, the technology can be used in water containing heavy metals, tannery and textile industry water treatment, food industry wastewater, paper industry wastewater, refinery wastewater or produced wastewater from oil and gas industry.
SIMPLE AND COST-EFFECTIVE COMPACT SYSTEMS
As a pioneer in compact wastewater chemical plant technology, VentilAQUA developed the Compact Unit of physical-chemical wastewater treatment solutions, which have proven to be an effective solution in every application around the world. As a result, industrial wastewaters coming from different sources can be easily treated or pre-treated in a simple and compact system, to be able to comply with sewage discharge regulations or environment discharge limits. Furthermore and most commonly, treated waters can be recovered to different industrial processes. The ecological and economic advantages of the compact systems, open up new possibilities for many users to treat their industrial wastewaters, simply, with low investment, cost-effective, in an easy friendly structure, with low space requirements, small footprint, etc.

AUTOMOTIVE CASE STUDY
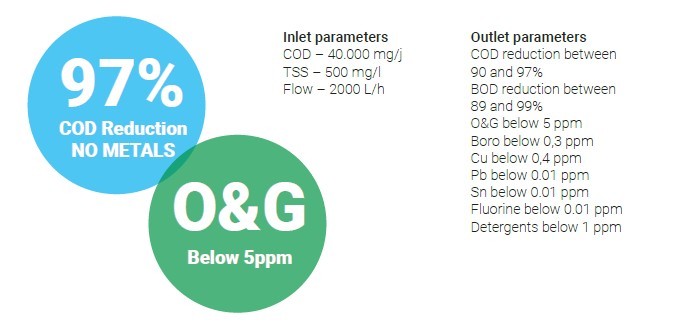
Automotive/Aeronautic/Metal industry (cars, trucks, planes, heavy machinery, components) faces increasing environmental requirements, especially on COD, metal removal and special molecules removal. Often residual metal levels, residual hydrocarbon or oil levels or surfactant content are a problem which traditional chemical or biological treatment plants cannot solve. Often a good and effective
treatment plant can no longer comply with new requirements, coming either from authorities or even from internal goals and strategy. Most often, operating costs for existing plants are extremely high.

Metal removal is easy as fast forward with electrocoagulation. Oils and emulsion removal also. No more huge chemical dosage, no more huge activated carbon adding, no more pH control up and down is required.

Introducing advanced oxidation systems to these operations is the key to solve these problems, either along with new treatment plants or just revamping/retrofitting existing ones. Very short paybacks on investment with these revamping are quite common.
Many companies use very expensive final or tertiary treatment procedures, like activated carbon adsorption, to try to solve these problems, most of the times unsuccessfully at a very high cost. VentilAQUA’s AOP solutions with electrocoagulation show the way to metal, oils and emulsion removal. No more huge chemical dosage, no more huge activated carbon adding, no more pH control up and down is required.
CHEMICAL & PHARMA INDUSTRY
CASE STUDY
In recent years, the number, variety, and composition of synthetic chemical compounds have increased tremen- dously. Their use has influenced every aspect of modern life. A particularly widespread group of chemical com- pounds are phenolic resins (phenol-formaldehyde resins or bakelite). They have been reported to have high stability and high environmental toxicity. Additionally, carcinogenic properties can damage human health seriously. The phenol formaldehyde resin producing industries generate waste- water with a high concentration of organic matter. Such wastewaters are difficult to be treated by biological processes when the phenol is present at high concentra- tion. The reason is that it causes inhibition to the normal function of the microbial population.

These technologies combined allowed for the total removal of formaldehyde and consequently, COD and BOD with a 99% removal. With these results, operating costs decreased a lot because all wastewater was being directed to a hazardous waste management company that charged for the transportation and treatment of the effluent. Such advantages in the cost of operation and construction will have a considerable weight on the economic balance of the project, in global terms.
The key to overcoming these problems lies in oxidative pre-treatment, such as adding electrocoagulation (EC) process before a biological one. EC is an electro-chemical process that removes suspended, emulsified or dissolved contaminants from water using an electric flow of charge. It generates a direct flow of charge to free into the liquid the metal ions from sacrificial anodes that will remove undesirable contaminants.

Inlet parameters
COD – 200.000 mg/L FORMALDEHYDE - 120.000 mg/L
Outlet parameters
COD - 1000 mg/L FORMALDEHYDE - <120 mg/L

SHOPPING MALLS & INDUSTRIAL KITCHENS
CASE STUDY
One of the most critical sources of environmental problems in any shopping center or mall is the food court, with its greasy waste waters. From a long term experience and survey, majority of malls and shopping centers have serious compliance problems with waters coming from grease traps. Grease traps are designed to retain waste waters for a period of time, generating bad odors and increasing organic loads that will
affect the downstream treatment plant, besides not com- plying with majority of reject limits for waste waters established by local authorities.

VentilAQUA brought to this process an advanced oxidation technology, using electricity, called electro-coagulation and electro-oxidation, which allows a more intense and efficient organic matter removal without chemicals, managing to reduce contamination to very low levels and allowing to use common multimedia filters with longer lifetime and to reuse these waters.
Under 1 year payback time with water consumption reduction, as about 90% of food court waste waters are recovered into flushing toilets, thus reducing dramatically water consumption in toilet rooms. Elimination of complex removal and trucking of liquid wastes and greases, highly loaded, and consequent extremely high cost.
Replacing standard or more sophisticated (although with limited performance) grease traps by chemical treatment units, with flotation devices (DAF), we manage to perform a proper chemical treatment to the waste waters, remove all solids, fats and greases, avoid bad odors, besides reducing drastically its organic loads, preparing these waters for a final disinfection and filltration which will allow them to be reintroduced into an internal feed line to flush waters and irrigation.


SILICA REMOVAL - REVERSE OSMOSIS
THE PROBLEM

With the rapidly increasing demands on water resources, the freshwater the shortage has become an important issue affecting the economic and social development in many countries. As one of the main technologies for producing fresh water from saline water and other wastewater sources, Reverse Osmosis (RO) has been widely used so far.
The presence of high silica concentrations in some brackish water, however, limits the application of RO desalination due to the potential formation of silica scales that irreversibly deteriorate the membrane material and performance.
SILICA REMOVAL - REVERSE OSMOSIS
On the other hand, 70% of industrial water is used as cooling water. However, cooling water recycling can lead to the concentration of dissolved species to a critical point of precipitation of insoluble mineral salts. Silica scale is a big technical challenge and a big financial burden for industrial operators since it has a dense and rigid physical form. It can reduce boiler power output by 10-20 % and thermal efficiency by 10%, even plug the pipeline, and increase shutdowns. Thus, it is urgent to remove silica from cooling water in order to recycle and reuse it.
SOLUTION

Electrocoagulation is an effective pre-treatment process to remove silica from the source brackish water. The effects of several electrical parameters, including electrode arrangement, current intensity and hydraulic retention time, were studied based on silica removal efficiency.
Total hardness (TH) and pH reduction is an essential pre-treatment step in water desalination plant (thermal or membrane, especially RO), to minimize precipitation of salts, and reduce operation/maintenance costs.
The electrocoagulation technique, as brackish groundwater pretreatment, can improve water quality by reducing TH, pH, electrical conductivity. Electrocoagulation is a technically feasible option to reduce silica concentration in cooling towers water. The application of this treatment could help to reduce the huge amount of makeup water usually demanded by cooling processes.
BELOW 5ppm
"It can achieve 75% TH removal rate, and pH reduction more than 2.4 degree, without any acidic addition, resulting in less secondary pollution and a huge cost savings"
“With electrocoagulation, for initial concentrations of dissolved silica between 80
mg/L and 200 mg/L, the removal efficiency can increase up to 80%.”

